
She put her nurses to work sanitizing the wards and bathing and clothing patients.
.jpg)
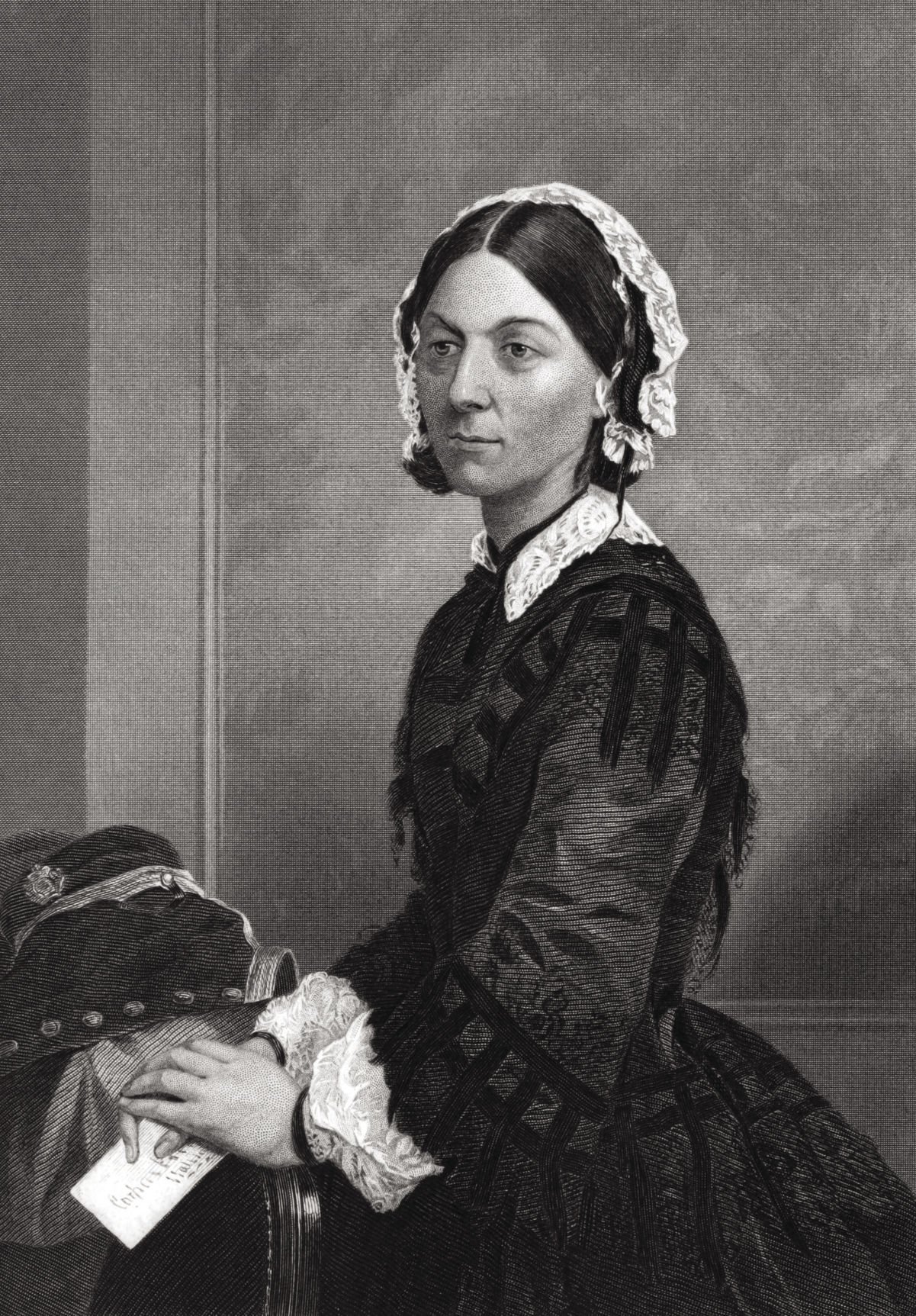
2Īlthough Nightingale did not accept the concept of bacterial infection, she deplored crowding and unsanitary conditions. According to Nightingale, the hospital case-fatality rate during the first months after her arrival was 32%. Sewage discharged onto floors of wards and dead animals rotted in the courtyards. The wards were vastly overcrowded, patients were covered with rags soiled with dried blood and excrement, the water supply was contaminated, and the food inedible. They found hospital conditions were far worse than reported. Nightingale and her team arrived in Turkey in November 1854. The Secretary was a friend of Nightingale's and knew her leadership skills. 1 Newspaper reports of unsanitary conditions at the military hospital had aroused the public, and the Secretary of War responded by appointing a team of nurses to address the situation. She first gained fame by leading a team of 38 nurses to staff an overseas hospital of the British army during the Crimean War. Her substantial contributions to health statistics are less well known. As member of parliament, McDonald introduced Canada’s groundbreaking health legislation, the Non-smokers’ Health Act, 1988, which led to smoke-free work and public places around the world.Florence Nightingale is revered as the founder of modern nursing. An environmentalist and political activist, she has served on the board of directors of Climate Action Network, Canada, and works on electoral reform, for proportional representation. McDonald is a former member of parliament and a former president of the National Action committee on the Status of Women, then Canada’s largest women’s organization. Her paperback, Florence Nightingale at First Hand (2010), gives highlights from the Collected Works series. She has published extensively on women theorists (three books and numerous articles), on political sociology, criminology and the environment. She did her PhD at the London School of Economics and has an honorary doctorate from York University, Toronto. Lynn McDonald, director of the Collected Works of Florence Nightingale, is university professor emerita at the University of Guelph, Ontario. All letters will be made available electronically (not all are in the published volumes, and for some excerpts were taken, to avoid repetition).
Who was florence nightingale full#
Electronic publication is planned of the names file (information on correspondents, colleagues, authors and experts cited), a full chronology of her letters, including incoming letters as well as her own, and events, and the transcription files themselves.

The Collected Works of Florence Nightingale Project website at the University of Guelph makes available free-of-charge short papers influenced by the series.

Print sources were also pursued for material, for sometimes a letter was available in a published source, but no manuscript could be found.Īll the volumes are available both in print and eBooks. Letters were obtained from over 200 archives worldwide. Many letters only arrived in archives generations later. She was famous in her lifetime and for years afterwards, so that people kept her letters and passed them on in the family. There is a “Dramatis Personae” at the beginning of each volume, and biographical sketches of major figures at the end of each.Įxtensive research was conducted to find Nightingale’s writing. Correspondents are identified, and, wherever possible, so also are persons mentioned in the letters or reports.
Who was florence nightingale plus#
They begin with background on her life and family (Volume 1), move through the influence of her faith (Volumes 2–4), her social science work (Volume 5), public health (Volume 6), European travels (Volume 7), women (Volume 8), two volumes on her India work (Volumes 9 and 10), her philosophical Suggestions for Thought (Volume 11), two volumes on civilian nursing (Volumes 12 and 13), and two on war: the Crimean War (Volume 14) and later wars (Volume 15), ending with hospital reform (Volume 16), a subject on which she worked throughout her professional life.Īll the volumes have comprehensive introductions, plus introductions to the major sections and individual letters or reports. The volumes are arranged thematically as listed below. It includes letters, most of them previously unpublished, short articles, pamphlets, letters-to-the editor and her full books and reports to government and royal commissions. The 16-volume Collected Works of Florence Nightingale (2001–2012) makes available for the first time the full range of Nightingale’s written work.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
